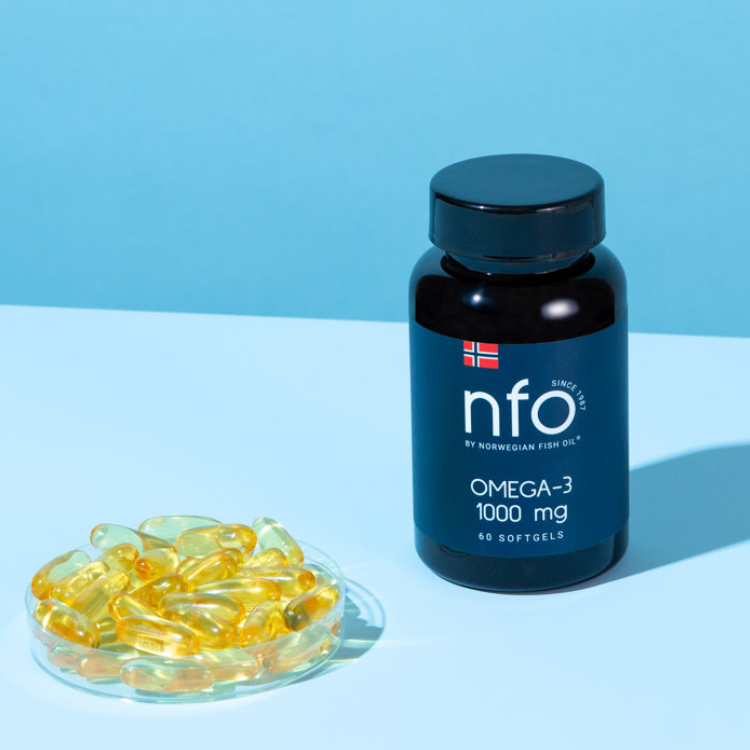
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. While lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management are key to managing blood pressure, certain supplements may also play a role in supporting healthy levels. This article explores the most effective supplements for managing high blood pressure, supported by scientific evidence, and highlights their mechanisms of action and safety profiles.
1. Magnesium
Magnesium is an essential mineral that helps regulate various physiological processes, including blood pressure. It relaxes blood vessels, reducing vascular resistance and thereby lowering blood pressure.
Research indicates that magnesium supplementation can significantly reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, particularly in people with magnesium deficiencies (Zhao et al., 2019). A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that daily magnesium intake of 300-500 mg for at least a month was associated with notable improvements in blood pressure levels (Rosique-Esteban et al., 2018).
2. Potassium
Potassium is another vital mineral that helps counteract the effects of sodium in the diet. It facilitates the excretion of sodium through urine and relaxes blood vessel walls, leading to lower blood pressure.
Several studies support the effectiveness of potassium supplementation in reducing hypertension. A systematic review concluded that increased potassium intake through diet or supplements lowers systolic blood pressure by 3-5 mmHg in hypertensive individuals (Aburto et al., 2013).
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, are well-known for their cardiovascular benefits. They reduce inflammation, improve endothelial function, and lower blood pressure by decreasing vascular resistance and improving arterial compliance.
A meta-analysis of 70 clinical trials revealed that daily doses of 2-4 grams of omega-3 fatty acids can reduce systolic blood pressure by an average of 4.5 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 3.0 mmHg (Miller et al., 2014).
4. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
CoQ10 is an antioxidant naturally present in the body and is involved in cellular energy production. Its antioxidant properties protect blood vessels from oxidative damage and improve endothelial function.
A systematic review of randomized controlled trials reported that CoQ10 supplementation could lower systolic blood pressure by up to 17 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by up to 10 mmHg (Rosenfeldt et al., 2007).
5. Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for bone health and immune function, but it also plays a role in cardiovascular health. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with increased risk of hypertension.
Supplementation with vitamin D may help regulate blood pressure by affecting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. A review of clinical trials found modest reductions in blood pressure with vitamin D supplementation, particularly in individuals with low baseline levels (Pilz et al., 2013).
6. Garlic Extract
Garlic has long been used in traditional medicine for its cardiovascular benefits. Garlic extract supplements contain allicin, a compound that helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
Studies suggest that garlic supplementation can reduce systolic blood pressure by an average of 7-10 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 5-6 mmHg (Ried et al., 2013). It is most effective when taken in doses of 600-1,200 mg per day.
7. Beetroot Extract
Beetroot is rich in dietary nitrates, which are converted into nitric oxide in the body. Nitric oxide relaxes blood vessels and improves blood flow, leading to lower blood pressure.
Clinical studies have shown that beetroot juice or supplements can significantly reduce systolic blood pressure by approximately 4-10 mmHg in hypertensive patients (Siervo et al., 2013).
8. L-Arginine
L-arginine is an amino acid that serves as a precursor to nitric oxide. By enhancing nitric oxide production, L-arginine supplements can help relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
A meta-analysis of clinical trials found that L-arginine supplementation at doses of 6-10 grams per day reduced systolic blood pressure by 5 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 3 mmHg (Dong et al., 2011).
9. Probiotics
Probiotics, commonly found in fermented foods and supplements, support gut health. Emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota influence blood pressure regulation.
A systematic review indicated that regular intake of probiotics, particularly those containing multiple strains, could lower systolic blood pressure by an average of 3.6 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 2.4 mmHg (Khalesi et al., 2014).
10. Hawthorn Extract
Hawthorn is a traditional herbal remedy for cardiovascular health. It contains bioactive compounds such as flavonoids and procyanidins, which improve blood vessel function and reduce blood pressure.
Research shows that hawthorn extract can moderately lower blood pressure, particularly when taken in doses of 900-1,800 mg per day (Walker et al., 2002).
Safety and Precautions
While these supplements can support blood pressure management, they should not replace prescribed medications or lifestyle changes. Consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or taking medications.
Conclusion
Supplements can play a supportive role in managing high blood pressure alongside a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management. Magnesium, potassium, omega-3 fatty acids, CoQ10, and other supplements mentioned above have shown promising results in scientific studies. However, individual responses may vary, and it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.