الإمساك مشكلة هضمية شائعة تصيب الأشخاص من جميع الأعمار. يتميز بحركات أمعاء غير منتظمة أو صعوبة في التبرز، وغالبًا ما يصاحبه شعور بعدم الراحة أو انتفاخ. في حين أن التغييرات الغذائية وزيادة شرب الماء غالبًا ما تكون الخطوات الأولى في علاج الإمساك، فإن المكملات الغذائية تلعب أيضًا دورًا هامًا في تخفيف الحالة. تستكشف هذه المقالة المكملات الغذائية التي قد تساعد في تخفيف الإمساك، مدعومة بأبحاث قائمة على الأدلة.
فهم الإمساك
قبل الخوض في تفاصيل المكملات الغذائية، من الضروري فهم أسباب الإمساك. تشمل الأسباب الشائعة قلة تناول الألياف، والجفاف، ونمط الحياة الخامل، والتوتر، وبعض الأدوية، والحالات الطبية الكامنة ( NIDDK، 2021 ). في حين أن الإمساك العرضي أمر طبيعي، إلا أن الإمساك المزمن قد يؤثر بشكل كبير على جودة الحياة وقد يتطلب رعاية طبية.
مكملات الألياف
1. السيليوم
السيليوم ألياف قابلة للذوبان، تُستخلص من قشور بذور لسان الحمل البيضاوي . يعمل السيليوم عن طريق امتصاص الماء في الأمعاء، مُكوّنًا مادة هلامية تُليّن البراز وتُعزز انتظام حركة الأمعاء. يُعدّ السيليوم فعالًا بشكل خاص في تحسين قوام البراز وتكرار خروجه ( ماك كوري وتشي، ٢٠١٦ ).
2. الإينولين
الإينولين هو ألياف بريبايوتيكية موجودة في نباتات مثل جذر الهندباء. يعزز نمو بكتيريا الأمعاء المفيدة، مما يُحسّن انتظام حركة الأمعاء ( فانديبوت وآخرون، ٢٠١٧ ).
3. ميثيل السليلوز
ميثيل السليلوز ألياف شبه صناعية تمتص الماء لزيادة حجم البراز. وهو أقل عرضة للتسبب بالغازات أو الانتفاخ مقارنةً بمكملات الألياف الأخرى ( ماك كوري وآخرون، ٢٠١٩ ).
مكملات البروبيوتيك
1. بيفيدوباكتيريوم لاكتيس
تُحسّن هذه السلالة من البروبيوتيك من وتيرة التبرز وتُقلّل من زمن عبور البراز. وقد أظهرت الدراسات فعاليتها في تخفيف الإمساك ( فورد وآخرون، ٢٠١٤ ).
2. لاكتوباسيلوس رامنوسوس
تدعم هذه السلالة انتظام حركة الأمعاء من خلال تعزيز حركة الأمعاء ( Zhu et al.، 2019 ).
مكملات المغنيسيوم
1. سترات المغنيسيوم
يعد سترات المغنيسيوم خيارًا شائعًا لتخفيف الإمساك العرضي عن طريق سحب الماء إلى الأمعاء ( شيلر، 2018 ).
2. هيدروكسيد المغنيسيوم
يُعرف عادةً باسم حليب المغنيسيا، ويعمل كملين أسموزي فعال ( شيلر، 2018 ).
المكملات العشبية
1. السنا
يحتوي السنا على السينوسيدات، التي تحفز تقلصات الأمعاء وتعزز حركة الأمعاء ( Nieber، 2017 ).
2. الصبار
يحتوي الصبار على أنثراكينونات ذات تأثيرات مُليّنة. مع ذلك، يُنصح بتجنب استخدامه لفترات طويلة نظرًا لآثاره الجانبية المحتملة ( أولبريشت وآخرون، ٢٠٠٨ ).
مكملات غذائية مفيدة أخرى
1. فيتامين سي
يمكن لجرعات عالية من فيتامين سي أن تعمل كملين أسموزي عن طريق سحب الماء إلى الأمعاء ( Rosenberg et al., 2016 ).
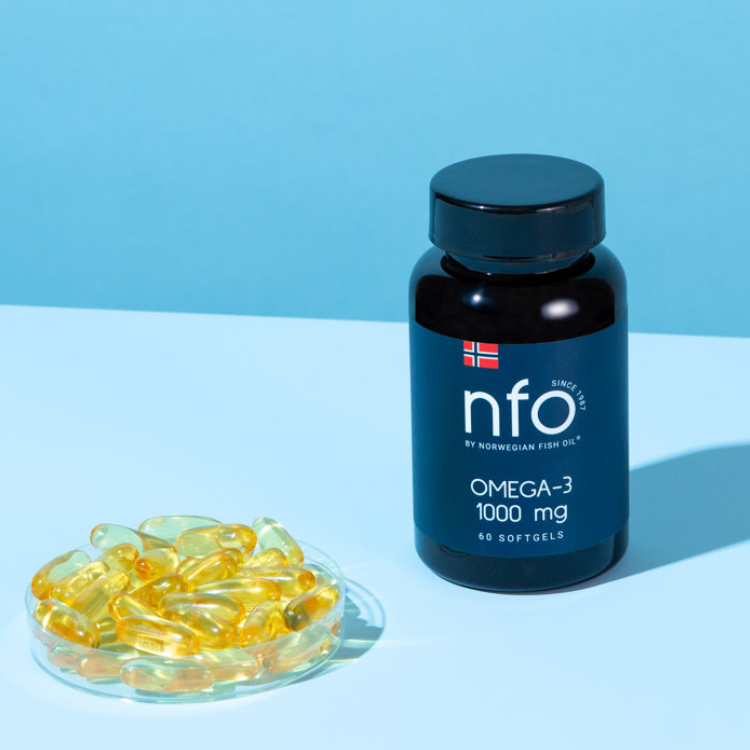
2. أحماض أوميغا 3 الدهنية
قد تعمل أحماض أوميجا 3 الدهنية الموجودة في زيت السمك على تحسين حركة الأمعاء ( Mishra et al., 2017 ).
3. مستخلص البرقوق
تحتوي مكملات مستخلص البرقوق على نسبة عالية من السوربيتول، الذي يساعد على تحسين قوام البراز وتكراره ( Attaluri et al., 2011 ).
السلامة والاعتبارات
رغم فعالية المكملات الغذائية، إلا أن الإفراط في استخدامها أو استخدامها بشكل غير صحيح قد يؤدي إلى آثار جانبية. استشر طبيبك دائمًا قبل البدء بتناول أي مكمل غذائي، وحافظ على رطوبة جسمك، والتزم بالجرعات الموصى بها.
خاتمة
يمكن أن يؤثر الإمساك بشكل كبير على الحياة اليومية، لكن المكملات الغذائية كالألياف والبروبيوتيك والمغنيسيوم والعلاجات العشبية تُخففه بفعالية. بالجمع بين المكملات الغذائية وتغييرات نمط الحياة كالترطيب الجيد واتباع نظام غذائي متوازن، يُمكن تحسين صحة الجهاز الهضمي على المدى الطويل.